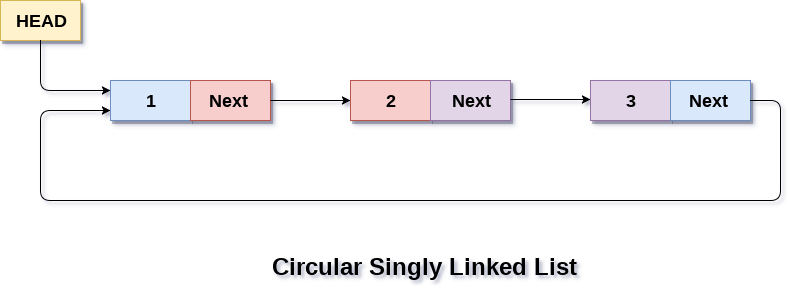
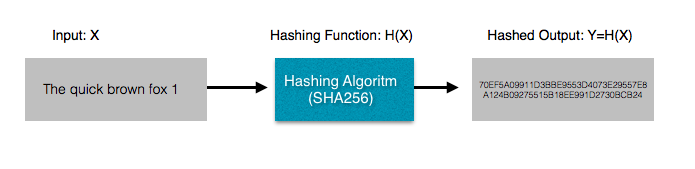
AVL Tree
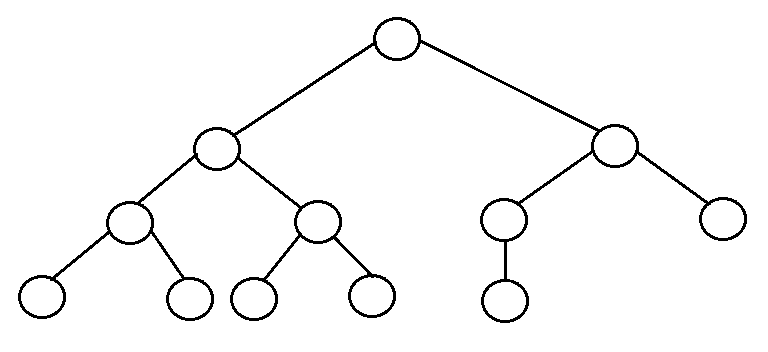
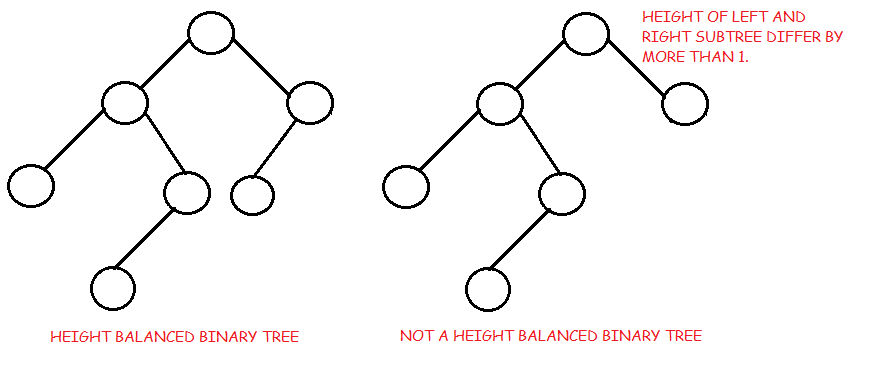
AVL tree is a self-balancing Binary Search Tree (BST) where the difference between heights of left and right subtrees cannot be more than one for all nodes.
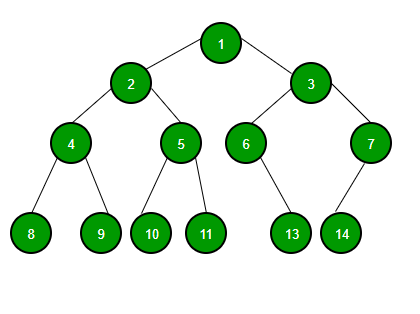
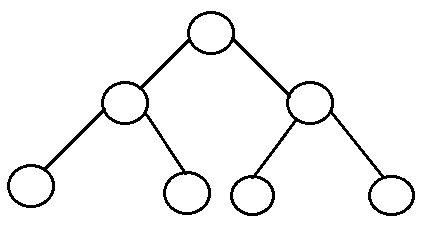
Example of Tree that is an AVL Tree
The tree above is AVL because the difference between heights of left and right subtrees for every node is less than or equal to 1.
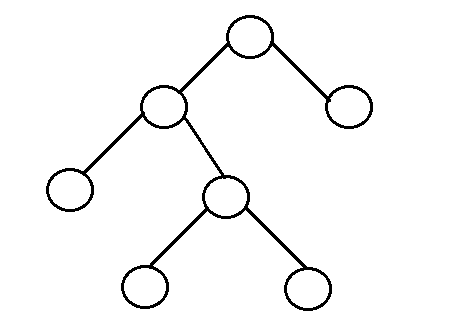
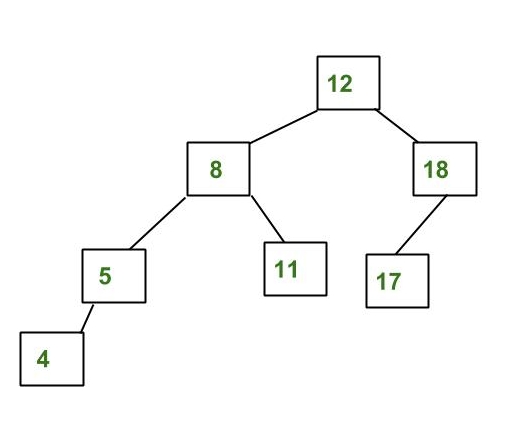
Example Tree that is not an AVL Tree
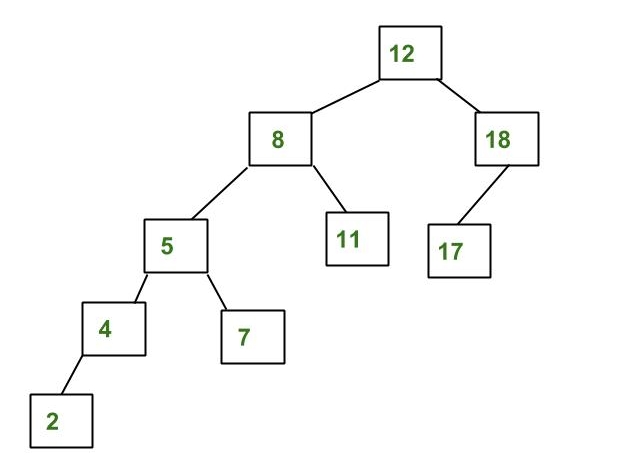
The tree above is not AVL because the differences between heights of left and right subtrees for 8 and 18 is greater than 1.
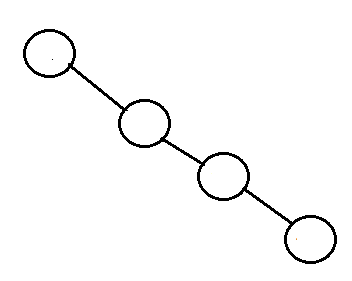
Most of the BST operations for example search, max, min, insert, delete, etc. take O(h) time where h is the height of the BST. The cost of these operations may become O(n) for a skewed Binary Tree. If we make sure that height of the tree remains O(Log n) after every insertion and deletion, then we can guarantee an upper bound of O(Log n) for all these operations. The height of an AVL tree is always O(Log n) where n is the number of nodes in the tree.
Source: